BERLIN - Development of nanogrid technology and its relation to the energy efficiency of buildings
BERLIN project is all about cost-effective rehabilitation of public buildings into smart and resilient nano-grids using storage. How does this technology work?
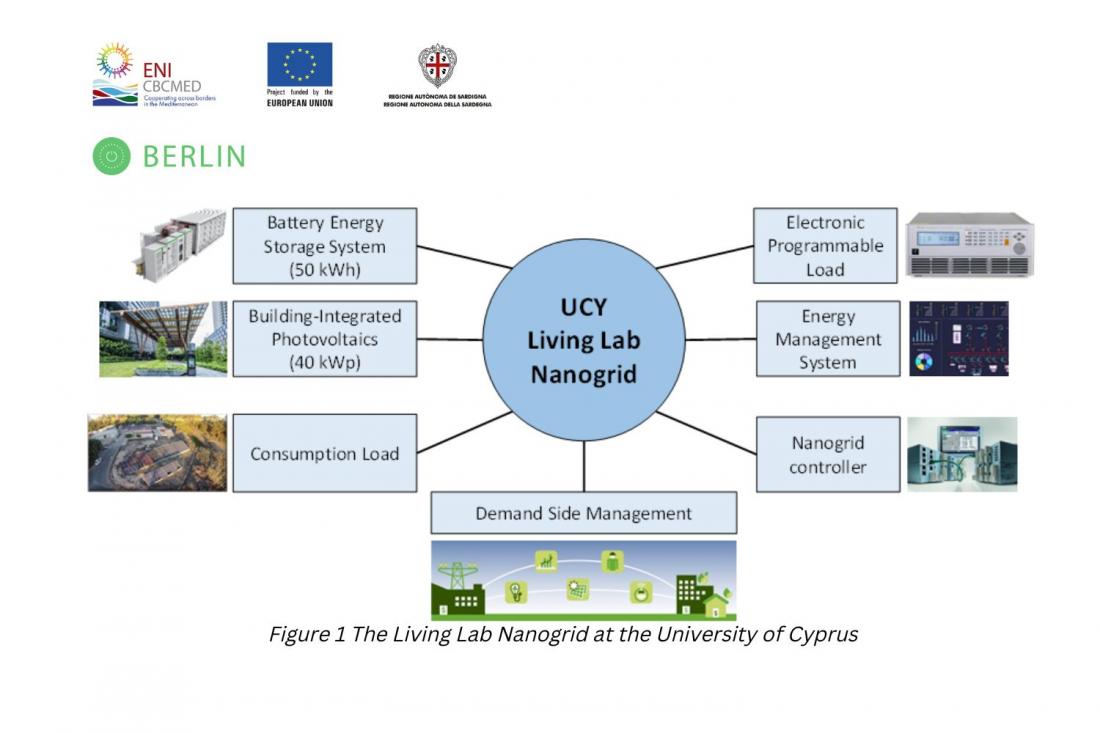
In simple terms, a nanogrid is a small-scale, decentralized power grid which can operate autonomously, but can also remain connected to the central power grid. A nanogrid can be based on sustainable electricity sources like solar Photovoltaics (PVs), and can integrate them with energy storage technologies, like batteries, and energy management strategies to maximize efficiency and minimize power imports and exports to the central power grid. The BERLIN project combines three key technologies, namely: PVs, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) and Demand-Side Management (DSM).
The nanogrid under development at the University of Cyprus (UCY) will convert the existing PV lab into a Living Lab nanogrid. The purpose of the UCY nanogrid is to minimize the interaction with the central power grid with onsite generation of green electricity through solar PV panels and also energy storage through BESS. Additionally, DSM strategies will be adopted to the nanogrid to help optimize its operation and move towards a completely self-sufficient operational pattern.
The nanogrid is expected to have a huge impact in the development of novel integrated energy systems and set a new paradigm for the future energy infrastructure of Cyprus and the Mediterranean area. Specifically, the nanogrid serves two main purposes: (a) it will increase the self-sufficiency level of the PV lab through onsite generation, storage, and consumption, with minimum dependence from the central power grid, and (b) it will allow the researchers of the PV lab to operate the nanogrid system, conduct various tests on the system components, and take valuable experimental data.